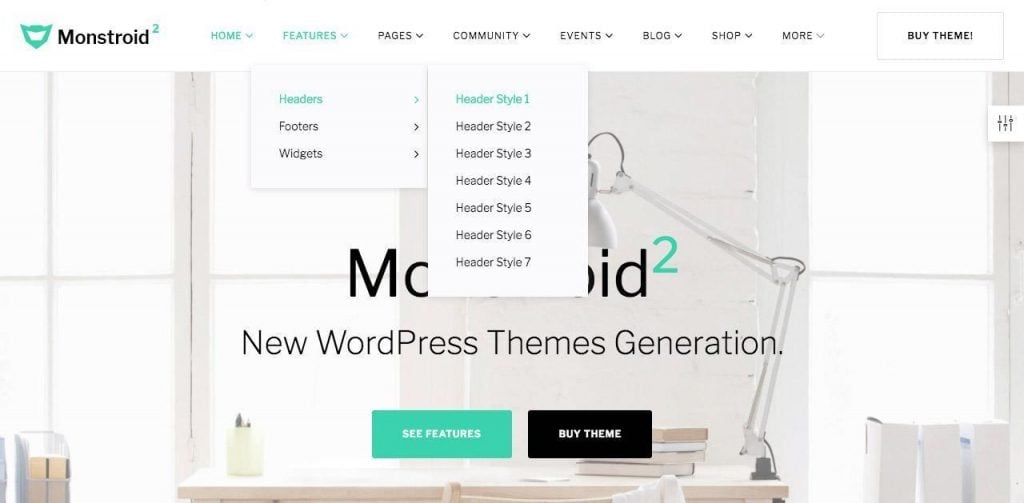
Creating a WordPress Navigation for your Theme
Menus in WordPress are a powerful tool. They let users quickly create navigation menus from their WordPress post data. They’re also a common obstacle for those just getting into theme development.
If you’re used to developing menus with just HTML you’ve likely been building out your menu markup something like this:
class="nav-wrapper">
id="site-navigation">
class="menu-item"> href="/">Home
class="menu-item"> href="/about.html">About
class="menu-item"> href="/contact.html">Contact
When converting that markup to a WordPress theme, I’ll commonly see developers use functions like get_permalink() to set the href attribute for each link.
That works, but it locks your user into that navigation and doesn’t take advantage of WordPress’s powerful menu editing features. If they decide to create a new About Us page in WordPress suddenly the get_permalink() call using the old page ID doesn’t work.
That’s no fun for anyone.
I also wonder if you’ve already heard of our new subscription service ONE. If no, keep reading! ONE is a great chance to save your money and get more products from Templateog体育首页. Do you know why? Because ONE can give you an opportunity to download any items from ONE package with no restrictions for only $19 a whole month. The main plus of the service is the chance to have a lot of themes, plugins, templates and the opportunity to use them, and then to choose the best one for a website. As WP are very cool and popular themes now, I recommend you to check out what we have now from WordPress themes in the pack. If you are a blog reader, you can grab a 5% discount using the promo code BecomeThe1.
Doing menus the WordPress Way(TM)
The proper way for displaying navigation menus in WordPress is to use the wp_nav_menu() function.
Calling this function with a registered menu outputs all the markup for your navigation. Plus, it will add classes for current pages and the ancestors of current pages all based off what a user enters in the Appearance > Menus settings screen.
You may have caught that little reference to a registered menu and thought, “Yeah but how do I register a menu?” You’ve got a keen eye. Was it the link that gave it away?

Registering a Menu Location
Before you start outputting menus into your WordPress theme, you’ll need to register the menu location for the navigation. There are two functions provided by WordPress to handle this, register_nav_menus() and register_nav_menu(). The main difference being the former allows you to register multiple menus using an array. We’ll use that one.
Let’s say we want to create a new menu location to use for our primary site navigation. First, we need to hook a custom function into WordPress’s init action. We can do that with the following code in your functions.php file:
add_action( 'init', 'theme_prefix_register_menus' );
Now we need to create the theme_prefix_register_menus() function.
function theme_prefix_register_menus() {
register_nav_menus(
array(
'primary_menu' => __( 'Primary Menu', 'theme_prefix' ),
)
);
}
Note: Replace “theme_prefix” with a string unique to your theme. You should be doing this on all functions registered within your theme for consistency.
Great! Now your full code in your functions.php file should look like this:
function theme_prefix_register_menus() { register_nav_menus( array( 'primary_menu' => __( 'Primary Menu', 'theme_prefix' ), ) ); } add_action( 'init', 'theme_prefix_register_menus' );
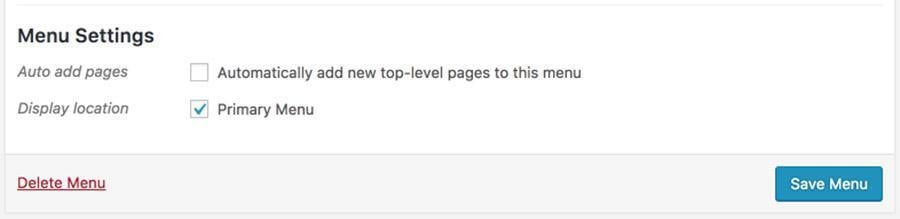
Now when editing menus in your Appearance > Menus edit screen in the dashboard, you’ll see a checkbox to set that menu to your Primary Menu location.
Displaying Menus on your WordPress Theme
Ok, now that we’ve registered a menu we want to display it on our theme.
To do that we just need to use the wp_nav_menu() function with the theme_location argument set to primary_menu.
wp_nav_menu( array ( 'theme_location' => 'primary_menu ) );
That’s it. With that called our theme would now display the menu set to the Primary Menu location in our Menus edit screen. If the user doesn’t set one, the above function would fallback to use wp_page_menu() which displays a list of all your Pages.
That might not be your desired fallback, but we can control that as well as a few other useful features with added parameters passed to the wp_nav_menu arguments array. Let’s go through a few useful ones.
menu_id - Set the ID to be used on the menu
- element. This defaults to the menu slug. primary_menu in our example.
- element as a
container - Setting this allows you to wrap the
- in a specific element. This defaults to
container_class - This allows you to set a class to be applied to your container element. For example, if we wanted to wrap our nav in
we’d set this to nav-wrapper.fallback_cb - This fires a function if the menu doesn’t exist. It defaults to display all pages using wp_page_menu. If you wanted nothing to return you would set this to false. Alternatively, you could wrap your wp_nav_menu call in a has_nav_menu conditional statement.
For a full list check out the Codex for wp_nav_menu.
So, let’s put that all together and generate the markup for our original HTML menu.
wp_nav_menu( array( 'theme_location' => 'primary_menu', 'menu_id' => 'site-navigation', 'container' => 'nav', 'container_class' => 'nav-wrapper', 'fallback_cb' => false ) );
Now we should be getting HTML markup like our original HTML menu.
Styling your WordPress Menu
Now that you’ve got the markup output for your WordPress menu you’ll want to style it.
Links, Active States, Hovers, and Focus. Oh, my!
One of the wonderful things about using WordPress’s built-in menu functionality is that it applies various classes to your items for tracking which menus items are active or have active child menu items. These can be used to adjust the styles of items to show users where they are on the site.
Here are a few of the more useful items for figuring out where a user is currently located on the site.
.current-menu-item - This class is added to the menu item that corresponds to the page that is currently being displayed.
.current-menu-parent - This class is applied to the hierarchical parent of the currently rendered page. For example, if your About page had a child page of Contact Us, then when you’re on the Contact Us page your Contact Us menu item would have the class .current-menu-item and your About menu item would have .current-menu-parent.
.current-menu-ancestor - This class works similar to .current-menu-parent except it goes multiple levels up the page hierarchy. In our About example, if we added a child page to Contact Us we’d then have the following classes on our menu items.
About - .current-menu-ancestor
Contact Us - .current-menu-ancestor .current-menu-parent
Third Level Page - .current-menu-item
These classes provide you great power in creating accessible and easy to use navigation menus that keep your user informed on where they are on your site.
For a list of all classes added to menu items see the Codex.
As you build navigation menus as well, you should keep in mind that some users may be navigating your menu with only a keyboard. That means you should include :focus states alongside your :hover states so keyboard-centric users know which menu item they’re currently on.

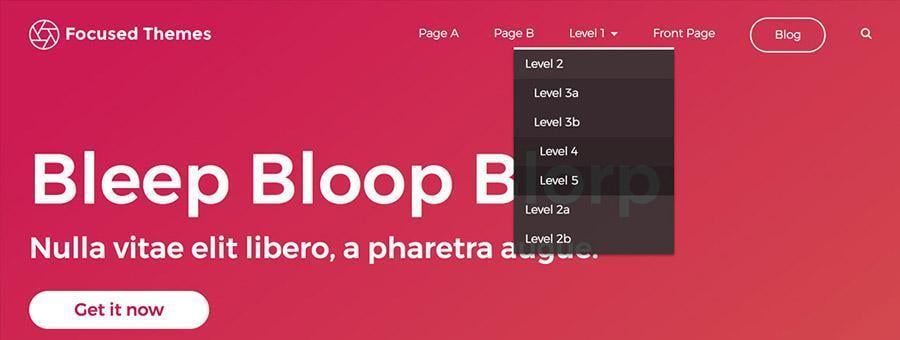
Sub Menus and Dropdowns
Another nice element of the WordPress menu markup is that any nested menus are added within their parent
Get more to your email
Subscribe to our newsletter and access exclusive content and offers available only to og体育首页Post subscribers.